About RIF Gateways
RIF Gateways develops easy-to-use tools and technologies that allow developers and companies to design blockchain-based applications that can seamlessly interact with the external world.
RIF Gateways leverages the latest advances in research and integrates the most widely-recognized industry solutions, providing at the same time a unified and common interface layer which reduces the complexity of implementing these technologies. It allows consumers and providers to easily set up secure and reliable data transfers supporting a wide range of data consumption, subscription, and payments models.
RIF Gateways is structured into 3 core services:
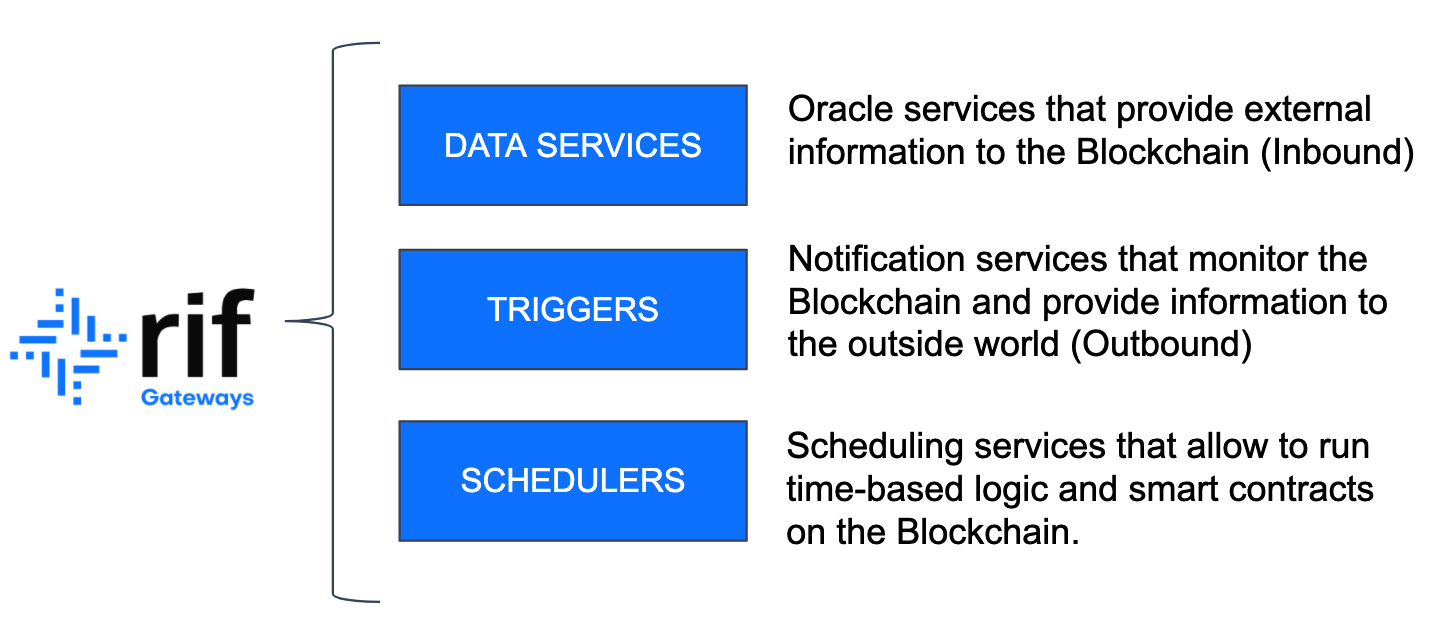
Data Services
RIF Data Services manages the information coming from the external world into the Blockchain (Inbound transactions). These are also commonly known as “Oracles” and allow smart contracts to run business logic based on external information. Some examples of applications that typically require external data are insurance contracts (which may need information about external events and pay whenever a specific chain of events takes place) or finance applications (which usually involve contracts that need access to price feeds and exchange rates such as USD/EUR), among others.
Triggers
RIF Triggers deals with information flowing from the blockchain into external applications and systems (outbound transactions). Traditional applications also need to access data generated within the blockchain in order to perform their logic and operations. Some examples are gaming applications, which have to process smart contract events in order to show specific updates to the participants, and payment applications, which require alerts and notifications anytime funds are received/withdrawn from certain accounts.
Schedulers
RIF Schedulers takes care of periodic and recurring transactions, allowing users to run time-based logic and smart contracts on the blockchain. There is a need for most applications to be able to execute transactions based on certain time conditions and this feature is not natively-supported in any blockchain. An example of this could be an investment application, which requires a smart contract to payout earnings and rewards to contributors at the end of a certain period.