Registry
The RNS Registry is the contract that stores the ownership of the nodes.
Registry mainnet
- Address:
0xcb868aeabd31e2b66f74e9a55cf064abb31a4ad5 - ABI: RNSABI.json
See RNS Testnet section for testing environment information.
Index
- Abstract
- Acquire a domain
- Change the Resolver
- Transfer ownership
- Release a domain ownership
- Structure
- Methods
Abstract
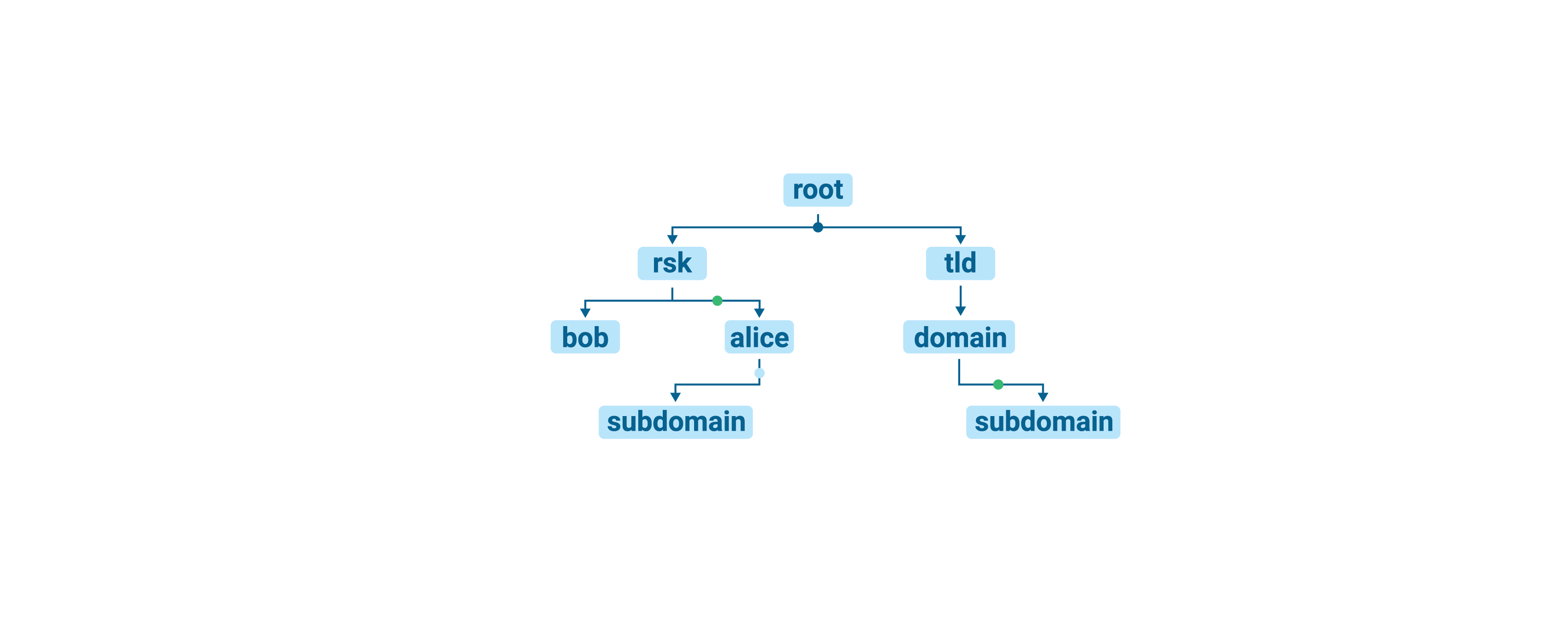
Node
The node is the main structure of the RIF Name Service Registry. A node has an owner, a Resolver and a time to live (TTL). A node owner can:
- Register sub nodes derived from it, with their owners
- Set the node's Resolver: Resolvers are responsible for performing resource lookups for a name - for instance, returning a contract address, a content hash, or IP address(es) as appropriate.
- Set the node's TTL: the caching time-to-live.
- Transfer node's ownership
The root node
The root node is the parent of top-level domains. This node is located in the 0x00 position of the Register, and its owner is the Registry deployer.
Top level domains
Top level domains are nodes derived from the root node. These domains are set in the Registrar contract deployment. RNS top level domain is rsk. The rsk top level domain name-hash is stored in the Registry contract.
Domains
Domains are acquired by winning an auction in the Registrar contract. When the auction is finalized, a new record is stored in the Registry contract, derived from the rsk top level domain. This registered domain has the Deed owner as default owner, and its parent Resolver as the default Resolver.
Subdomain
Once a domain is registered in the Registry, the owner can create subdomains derived from it. This will register new nodes in the Registry. Each of this sub nodes have the same characteristics of the parent node: it's owners may create sub nodes derived from it, or transfer the sub node's ownership.
Acquire a domain
There are 3 ways to acquire a domain:
- Win an auction for an open domain (view Registrar contract)
- Be delegated a subdomain
- Be transferred a domain
Set a subdomain
Subdomain creation is made through the setSubnodeOwner method of the Registry. Let's see an example:
const node = namehash('nakamoto.rsk');
const label = web3.sha3('satoshi');
const owner = '0xc5032...';
const newOwner = '0x23fb8...';
rns.setSubnodeOwner(node, label, newOwner)In this example we are adding the entry 'satoshi.nakamoto.rsk' to the Registry and assigning ownership of it to '0x23fb8...'. The subdomain is created using its parent Resolver.
Then, we can query:
var owner = rns.owner('satoshi.nakamoto.rsk')
// 0x23fb8...The new subdomain behaves as any node, so its new owner can repeat the process and create new subdomains under that node, for example 'wallet.satoshi.nakamoto.rsk' or 'donations.satoshi.nakamoto.rsk'. Also the new owner is the one who can change the Resolver.
The owner of the original domain can call setSubnodeOwner at any time and override ownership of their subdomain, removing '0x23fb8...' as the owner of 'satoshi.nakamoto.rsk'. However, the sub-subdomains previously created will still exist, so unless the domain owner overrides ownership of them, they will keep resolving to their configured address.
Change the Resolver
Once you gain ownership over a domain you must configure the name resolution for said domain. For more information about resolutions have a look at Resolver contract and 'Resolving a name'.
var node = namehash('adomain.rsk')
var newResolverAddress = '0xe87ba...'
rns.setResolver(node, newResolverAddress)Now that the resolver is configured, you have to configure which is the desired domain it has to resolve to. This is done using the setAddr method:
var node = namehash('adomain.rsk')
var resolverAddress = rns.resolver(node)
var resolverInstance = web3.contract(resolverAddress)
var resolver = resolverInstance.at(resolverAddress)
var resolveTo = '0x9eb63...'
resolver.setAddr(node, resolveTo)Transfer ownership
Any entry from the Registry, domain or subdomain, can be delegated through the setOwner method. However, in the case of domains gained through auctions, this won't update the information at Registrar or Deed level, so the owner won't be allowed to perform auctions such as releasing the domain.
A full domain transference should be done through the transfer method of the Registrar, which handles not only the Registry update but changes the owner of the Deed as well. Note that when transferring the Deed you are also transferring the tokens locked within it.
Release a domain ownership
A domain can be released at any point through the releaseDeed method of the Registrar. This closes the Deed, returning part of the funds to the owner, clears auction related values and deletes the entry from the Registry, returning the name to the Open state.
Structure
Types
struct Record {
address owner;
address resolver;
uint64 ttl;
}Storage
mapping(bytes32=>Record) records;For each namehash:
owner: the one who can perfomsetOwner,setTTL,setSubnodeOwnerorsetResolvermethods fo the namehashttl: the caching time-to-liveresolver: the address of the Resolver contract that resolves a specific domain
Methods
owner
Returns the address that owns the specified node.
function owner(bytes32 node) public view returns (address)setOwner
Transfers ownership of a node to a new address. May only be called by the current owner of the node.
Signature
function setOwner(bytes32 node, address ownerAddress) public only_owner(node)Parameters
node: the node to transfer ownership of.ownerAddress: the address of the new owner.
setSubnodeOwner
Transfers ownership of a sub node keccak256(node, label) to a new address. May only be called by the owner of the parent node.
Signature
function setSubnodeOwner(bytes32 node, bytes32 label, address ownerAddress) public only_owner(node)Parameters
node: the parent node.label: the sha3 hash of the label specifying the sub node.ownerAddress: the address of the new owner.
resolver
Returns the Resolver address for the specified node.
Signature
function resolver(bytes32 node) public view returns (address)setResolver
Sets the Resolver address for the specified node.
Signature
function setResolver(bytes32 node, address resolverAddress) public only_owner(node)Parameters
node: the node to update.resolverAddress: the address of the Resolver.
ttl
Returns the TTL of a node, and any records associated with it.
Signature
function ttl(bytes32 node) public view returns (uint64)setTTL
Sets the TTL for the specified node.
Signature
function setTTL(bytes32 node, uint64 ttlValue) public only_owner(node)Parameters
node: the node to update.ttlValue: the TTL in seconds.
setDefaultResolver
Sets the default Resolver for new nodes.
Signature
function setDefaultResolver(address resolver) public only_owner(0)Parameters
resolver: the address of the new defaultResolver